In an era of growing environmental concerns and the urgent need for sustainable solutions, Nature-based Solutions (NbS) are emerging as a promising approach to address a wide range of environmental challenges. However, the implementation of NbS is often influenced by government regulations and financial considerations. Join us on a journey to explore the role of government regulations surrounding NbS and how they can help, as well as the financial advantages of NbS compared to other green projects.
Government Regulations Surrounding NbS:
Policy Frameworks:

Governments play a crucial role in shaping the regulatory framework for NbS through policy development and implementation. This includes setting targets, establishing guidelines, and providing incentives to promote the adoption of NbS. For example, many countries have introduced policies to encourage the restoration of degraded ecosystems, such as wetlands and forests, through funding programs and tax incentives.
Permitting and Compliance:

The implementation of NbS projects often requires obtaining permits and complying with regulatory requirements, such as environmental impact assessments and land-use regulations. Governments play a key role in streamlining the permitting process and ensuring that NbS projects adhere to environmental standards and guidelines. This helps to protect natural resources and minimize potential negative impacts on ecosystems and communities.
Funding and Financial Incentives:

Governments provide financial support and incentives to facilitate the implementation of NbS projects. This may include grants, subsidies, and low-interest loans for NbS initiatives such as green infrastructure, reforestation, and coastal restoration. By investing in NbS, governments can achieve multiple objectives, including climate mitigation, biodiversity conservation, and disaster risk reduction.
Collaboration and Partnerships:

Governments collaborate with various stakeholders, including local communities, NGOs, and private sector entities, to promote the adoption of NbS and leverage additional resources and expertise. This collaborative approach fosters innovation, knowledge sharing, and capacity building, leading to more effective and sustainable NbS projects.
Now, let’s delve into how NbS can help address environmental challenges and achieve multiple objectives, including cost savings and financial benefits.
How Nature-based Solutions( NbS) Can Help:

Cost Savings:
One of the key advantages of NbS is its cost-effectiveness compared to traditional engineered solutions. NbS projects often require lower upfront capital investment and have lower operational and maintenance costs over their lifespan. For example, green infrastructure such as rain gardens and permeable pavements can reduce stormwater runoff and alleviate flooding at a fraction of the cost of traditional stormwater management systems.
Multiple Benefits:
NBS projects provide multiple benefits beyond their primary objectives, including improved air and water quality, enhanced biodiversity, and increased recreational opportunities. For example, urban green spaces not only help to mitigate urban heat island effects and reduce energy consumption but also provide valuable ecosystem services, such as carbon sequestration and habitat for wildlife.
Resilience and Adaptation:
NBS enhance the resilience of ecosystems and communities to climate change and natural hazards by restoring natural processes and ecosystem functions. For example, coastal restoration projects such as mangrove reforestation and coral reef rehabilitation help to protect coastal communities from storm surges, erosion, and sea-level rise while providing habitat for marine biodiversity.
Financial Comparison:
Let’s now compare the financial aspects of NbS projects with other green projects to understand their relative costs and benefits.
NbS vs. Traditional Infrastructure:

Studies have shown that NbS projects are often more cost-effective than traditional engineered solutions, particularly when considering their long-term benefits and ecosystem services. For example, Green infrastructure such as bioswales and vegetated rooftops can reduce stormwater runoff and alleviate flooding at a fraction of the cost of conventional stormwater management systems.
NbS vs. Grey Infrastructure:
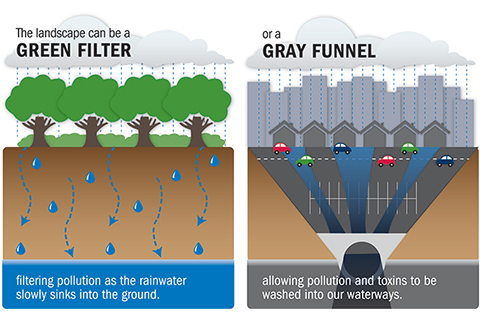
Nature-based Solution (NbS) projects also offer advantages over grey infrastructure in terms of cost savings, environmental benefits, and resilience to climate change. For example, coastal restoration projects such as wetland restoration and dune stabilization provide natural buffers against erosion and storm surges, reducing the need for costly seawalls and breakwaters.
NBS vs. Non-Green Projects:
When compared to non-green projects, such as conventional development or industrial activities, NbS projects offer significant financial advantages in terms of long-term sustainability and resilience. For example, investing in green infrastructure and sustainable land management practices can help to mitigate the adverse impacts of development on ecosystems and natural resources while providing multiple benefits to society.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, government regulations play a crucial role in shaping the regulatory framework for NbS and facilitating their implementation through funding, incentives, and collaboration. By promoting the adoption of NbS, governments can achieve multiple objectives, including environmental protection, climate mitigation, and economic development. Moreover, NBS projects offer financial advantages compared to traditional infrastructure and non-green projects, making them a cost-effective and sustainable solution for addressing environmental challenges and building resilience to climate change. As governments continue to prioritize sustainability and resilience in their policy agendas, the role of NbS will become increasingly important in shaping the future of our planet.
Learn more about Advantages and Disadvantages of Nature-based Solution (NbS), Click here

Written by
Anjeeta Goud
Team- Business development and Strategy
Terracon Ecotech.
Reference:
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-01241-2
https://unalab.eu/en/types-nature-based-solutions
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-01241-2
https://www.repsol.com/en/energy-and-the-future/future-of-the-world/nature-based-solutions/index.cshtml
https://www.repsol.com/en/energy-and-the-future/future-of-the-world/nature-based-solutions/index.cshtmlhttp://ience/nature-based-solutions/typeshttps://www.fema.gov/emergency-managers/risk-management/climate-resil




