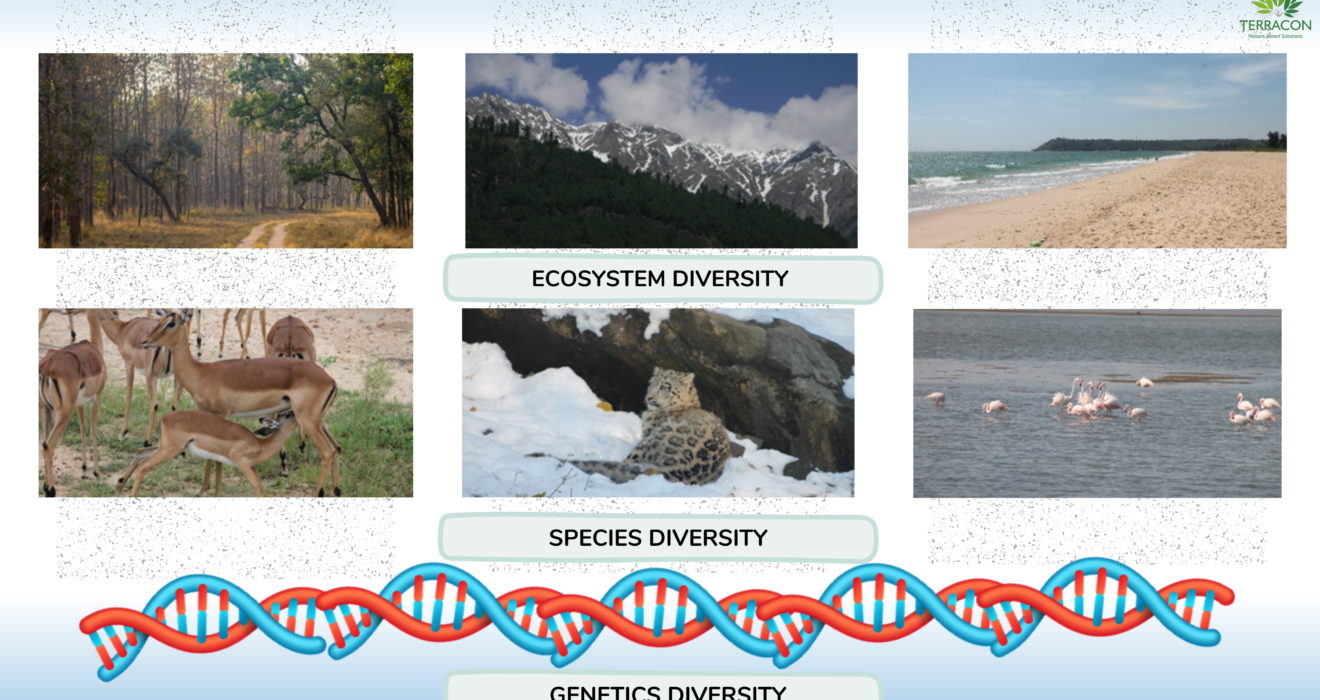
Introduction:
Global efforts to protect biodiversity are crucial for safeguarding the health of our planet’s ecosystems and combating the alarming rate of species extinction driven by human activities. The Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, published in 2019, served as a wake-up call by highlighting that up to one million species are at risk of extinction due to habitat destruction, pollution, overexploitation of resources, and climate change. These threats have significantly altered 75% of land-based environments and 66% of marine environments, endangering over 40% of amphibian species, nearly 33% of reef-forming corals, and one-third of marine mammals. Learn about Why Businesses Must Act Now To Protect Biodiversity?
Despite these challenges, global frameworks like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, adopted during the COP15 to the Convention on Biological Diversity, offer hope for reversing biodiversity loss by 2030. This framework sets ambitious targets, including conserving 30% of global terrestrial and marine areas, reducing pollution, and mobilizing funds for conservation efforts. By integrating biodiversity conservation into all societal sectors and prioritizing sustainable practices, these initiatives aim to ensure a resilient and healthy planet for future generations.
What efforts India has taken to Protect Biodiversity ?
India stands as a beacon of biodiversity conservation, with diverse sectors rallying to protect its natural treasures. From mining to forestry, pharmaceuticals to information technology, and tourism to hospitality, each sector plays a vital role in preserving the nation’s ecological balance. These sectors have made significant contributions, but they’ve also faced their fair share of challenges in the past. Despite these obstacles. they’re still dedicated to preserving our country’s biodiversity and making sure our environment stays healthy for generations to come.”
“Learn how local communities are leading the charge in biodiversity conservation, with insights from our latest blog
So let’s explore their impactful initiatives across sectors.

- Mining involves extracting valuable minerals from the Earth’s surface or underground, a process that often results in environmental consequences such as habitat destruction and pollution. These activities pose significant challenges, including habitat loss and water contamination. Studies show a decline in biodiversity hotspots and indicate that around 70% of water bodies near mining sites suffer from pollution.
In India, Coal India Limited, Vedanta Limited, and Hindustan Zinc Limited are leading mining companies contributing significantly to biodiversity assessment and conservation. With over 2 million trees planted and investments exceeding $5 million in biodiversity projects, these companies actively engage in habitat restoration and biodiversity monitoring. Through partnerships with local communities and conservation organizations, Hindustan Zinc demonstrates a commitment to responsible mining practices and environmental stewardship. Forestry manages forests sustainably, while logging is tree cutting for commercial use. Both are essential but need sustainable practices to protect forests and ecosystems.

- Forestry and logging are vital for managing forests sustainably and meeting commercial needs, respectively. However, both activities must adopt sustainable practices to safeguard forests and ecosystems. Despite their importance, the forestry sector faces significant challenges, including illegal logging and encroachment. Studies indicate that illegal logging constitutes a considerable portion, ranging from 50% to 90%, of total logging activity in certain regions.
In India’s forestry sector, the Birla Group , Adani Group is making significant strides in biodiversity assessment and conservation. Through initiatives like “Adani Harit,” the company has planted over 5 million trees across various states, contributing to ecosystem restoration. By collaborating with local stakeholders, Adani actively monitors biodiversity and promotes sustainable forestry practices, setting a commendable example for environmental stewardship.
- Pharmaceuticals are medications intended for medical treatment, prevention, diagnosis, or cure of diseases and health conditions in humans and animals. However, pharmaceutical companies encounter obstacles in contributing to biodiversity assessment due to regulatory complexities and logistical constraints. Obtaining permits for sourcing medicinal plants is time-consuming, and maintaining sustainable harvesting practices while meeting production targets presents a significant challenge.
Cipla Ltd, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Lupin Limited, are the largest pharmaceutical companies in India, is committed to biodiversity conservation through sustainable sourcing of medicinal plants. Lupin takes proactive measures to protect over 100 endangered plant species within its operations. Employing stringent responsible harvesting practices across 95% of its sourcing activities, Lupin ensures the preservation of delicate ecosystems and the promotion of biodiversity. By implementing measures to conserve biodiversity-rich areas, Lupin contributes to maintaining ecosystem health and preserving traditional medicinal knowledge.
- The Information Technology (IT) sector contributes to biodiversity conservation through technology-driven initiatives, such as data analysis tools and the promotion of eco-friendly practices within the industry. However, it faces challenges in implementing comprehensive environmental sustainability measures, including reducing carbon emissions and sourcing renewable energy, amidst rapid technological advancements and increasing energy demandsMindtree Limited, Wipro Limited, and Infosys, are multinational IT services company based in India, have made significant strides in environmental sustainability and biodiversity conservation. With a relentless pursuit of green initiatives, Infosys has achieved remarkable milestones, including a commendable 50% reduction in carbon emissions since 2015. Furthermore, Infosys has demonstrated its unwavering commitment to renewable energy by sourcing 100% of its electricity consumption from renewable sources. However, Infosys’s efforts do not stop there. The company actively engages in biodiversity conservation projects, undertaking tree plantation drives, ecosystem restoration initiatives, and the promotion of green infrastructure in urban areas. Through these endeavors, Infosys has planted over 500,000 trees and restored 20 hectares of degraded ecosystems, demonstrating its dedication to environmental preservation and ecosystem restoration.

- The tourism and hospitality sector includes businesses that offer services to travelers, such as accommodations, food and beverage services, transportation, entertainment, and leisure activities. However, these sectors face challenges in balancing tourism growth with environmental conservation and community well-being. Issues like over-tourism in ecologically sensitive areas and the need for sustainable tourism practices that benefit local communities while protecting natural resources are key challenges.
Lemon Tree Hotels , Radisson Hotel Group, and Taj Hotels, a subsidiary of Indian Hotels Company Limited (IHCL), are prominent players in the hospitality industry in India. With a firm commitment to responsible tourism practices, Taj Hotels has implemented initiatives like water conservation, reducing usage by 30%, and waste management, diverting 80% from landfills. Collaborating with communities, the company protects biodiversity, notably with 20 nature-based tourism activities and wildlife safaris for over 10,000 guests, fostering environmental stewardship.

India is like a treasure chest when it comes to different kinds of animals and plants. It has around 7-8% of all the different species found in the world! This means that out of every 100 species on Earth, about 7 or 8 can be found right here in India. This makes India super important when we want to learn about and protect different kinds of animals and plants everywhere. India shares important information about where these animals and plants live and how many of them there are with platforms like the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. These are like big libraries where scientists from all over the world can find information about different species.
For example, did you know that India has shared data on over 96,000 species with the GBIF? That’s a lot of information! This helps people all around the world understand how to take care of these animals and plants better. It’s like giving a big map to everyone to show which areas need the most help to keep nature safe and healthy.
The global biodiversity assessment has underscored the critical role of biodiversity in maintaining the health of our planet. These countries are chosen as examples to showcase a diversity of approaches and initiatives towards biodiversity conservation across different regions and ecosystems.

UK
- Approximately 28% of the UK’s land area is protected, including iconic sites like the Lake District National Park and Snowdonia.
- Schemes like Countryside Stewardship incentivize landowners to preserve habitats and wildlife.
- The UK is increasingly relying on renewable energy sources like wind and solar power.
- The government actively supports biodiversity conservation efforts to safeguard its diverse ecosystems.
US
- Over 10% of the US land area is designated as protected, including renowned areas such as Yellowstone National Park and the Everglades.
- Conservation programs like the Land and Water Conservation Fund provide funding for habitat preservation and restoration projects.
- The US is transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and hydroelectric power.
- Efforts are underway nationwide to mitigate human impacts on biodiversity and preserve natural habitats.


Brazil
- It’s home to the Amazon Rainforest, which is vital for biodiversity.
- The Amazon covers a huge area and hosts many unique species.
- Brazil has created protected areas within the Amazon to preserve its biodiversity.
- Even though there are challenges like deforestation, Brazil is working to protect its natural resources.
Norway
- Norway supports global conservation efforts.
- It has contributed over $1 billion to the Amazon Fund, which helps reduce deforestation.
- Organizations like the Rainforest Foundation Norway, backed by Norway, work to protect rainforests and indigenous rights.
- Norway also focuses on marine conservation, especially in the Arctic.


China:
- China has diverse ecosystems and many nature reserves.
- It created the Giant Panda National Park to protect pandas and their habitat.
- China is also reforesting areas to combat desertification and restore ecosystems.
Australia
- Australia is known for the Great Barrier Reef, home to thousands of marine species.
- The government has a plan, Reef 2050, to protect the reef by improving water quality and reducing pollution.
- Australia has established marine parks to safeguard marine life, including turtles and sharks.

Conclusion:
Global biodiversity assessments, rules, and regulations are critical for protecting the world’s biodiversity and ensuring its sustainability. Countries like the US and India have taken steps to protect their biodiversity, but more needs to be done to address the biodiversity crisis. Biodiversity affects daily life in many ways, and its loss can have negative impacts on human health and well-being.the future of biodiversity is facing a complex set of challenges and opportunities. Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, industrialization, and agriculture, are significantly altering natural habitats and putting immense pressure on biodiversity. Climate change exacerbates these threats, with rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events further stressing ecosystems worldwide.
The consequences of biodiversity loss are profound. It affects ecosystem services that are vital for human well-being, such as clean air and water, pollination, climate regulation, and disease control. Moreover, it undermines the resilience of ecosystems, making them more vulnerable to disturbances and less capable of adapting to changing environmental conditions.
However, amidst these challenges, there are reasons for hope. Global initiatives and frameworks, like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, set ambitious targets to reverse biodiversity loss and promote sustainable practices. These targets include conserving and restoring ecosystems, reducing pollution, and mobilizing resources for conservation efforts.
Furthermore, there is growing recognition of the intrinsic value of biodiversity and the need to integrate conservation into various sectors, including agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and urban planning. Community-based conservation initiatives and indigenous knowledge systems also play a crucial role in protecting biodiversity and maintaining traditional ecological practices.
Overall, the future of biodiversity depends on collective action and a holistic approach that addresses the underlying drivers of biodiversity loss while promoting sustainable development. It requires collaboration among governments, civil society, businesses, and individuals to safeguard the rich tapestry of life on Earth for current and future generations.

Written by
Anjeeta Goud
Team- Business development and Strategy
Terracon Ecotech
Reference:
https://www.cbd.int/doc/press/2019/pr-2019-05-06-IPBES-en.pdf
https://www.globallandscapesforum.org/publication/the-global-assessment-report-on-biodiversity-and-ecosystem-services/
https://cites.org/eng/news/major-new-global-assessment-describes-biodiversity-in-crisis_06052019
https://www.ipbes.net/global-assessment
https://unctad.org/topic/trade-and-environment/biotrade/kunming-montreal-global-biodiversity-framework#:~:text=The%20Kunming%2DMontreal%20Global%20Biodiversity,the%20Convention%20on%20Biological%20Diversity.
https://www.iucnredlist.org/
https://forestsclearance.nic.in/DownloadPdfFile.aspx?FileName=1111112461216M3AIEbio.pdf&FilePath=../writereaddata/wildlife/Userdetail/
https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/Rep-2000-055.pdf




