The urban environment is facing a major challenge. As cities grow and develop, they often become crowded and lack green areas. This can lead to problems for the people living there, such as feeling stressed and anxious, dealing with hot temperatures due to urban heat islands, and losing natural habitats and ecosystems. Trees play a vital role in mitigating these effects by not only beautifying our cities but also providing crucial services such as shade, cooling, and habitat provision, and help keep our environment balanced. To make cities more livable, it’s important to prioritize creating and preserving urban parks and gardens, green corridors, and tree-lined streets. Learn about the role of trees in improving air quality and reducing pollution in urban environments.
Challenges in Urban Environments
However, many cities in India face pressing challenges due to rapid urbanization, often replaces natural green spaces with concrete structures like buildings and roads, leading to several critical environmental challenges. Read about successful tree planting initiatives and their impact on biodiversity conservation. Firstly, the loss of greenery reduces the capacity of urban areas to absorb pollutants, resulting in poor air quality and increased respiratory diseases among residents. Secondly, urban heat islands exacerbate temperatures in densely built areas, raising the risk of heat-related illnesses. Thirdly, biodiversity loss occurs as natural habitats are fragmented, impacting ecosystem health and reducing opportunities for urban residents to access natural spaces. Addressing these challenges requires prioritizing green infrastructure and sustainable urban planning to mitigate environmental impacts and improve public health outcomes in Indian cities.
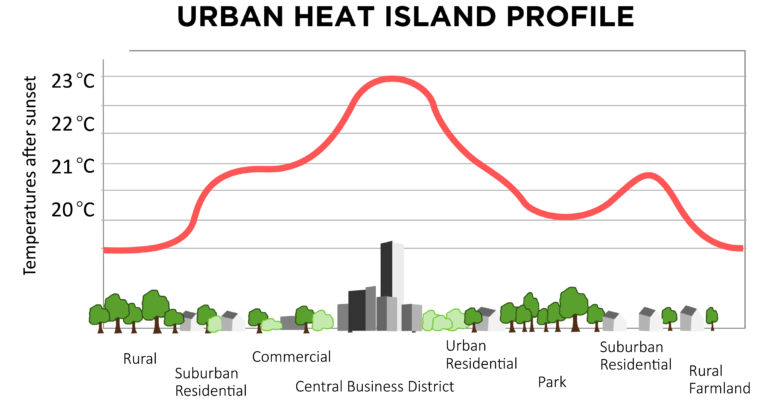
Trees reduce the ‘heat island’ effect caused by pavement and buildings in urban areas, cooling the city by up to 10°F.
What is the role of Tree Census in Urban Planning?
Tree census initiatives serve as vital tools for urban planners to understand and manage urban green spaces effectively. By conducting systematic surveys of tree populations, cities gain valuable insights into the distribution, species diversity, and health status of trees across different neighborhoods. This data empowers planners to make informed decisions on where to plant new trees, prioritize areas for green infrastructure development, and allocate resources strategically. Learn what is Tree Census?
Recent studies underscore the significance of urban trees in mitigating environmental impacts and enhancing urban livability. For instance, research shows that strategically placed trees can reduce urban air temperatures by up to 2-8°Celsius, significantly lowering cooling costs for buildings and improving outdoor comfort for residents. In terms of air quality, trees absorb pollutants such as carbon dioxide, ozone, and particulate matter, thereby improving overall air quality and reducing respiratory health risks.
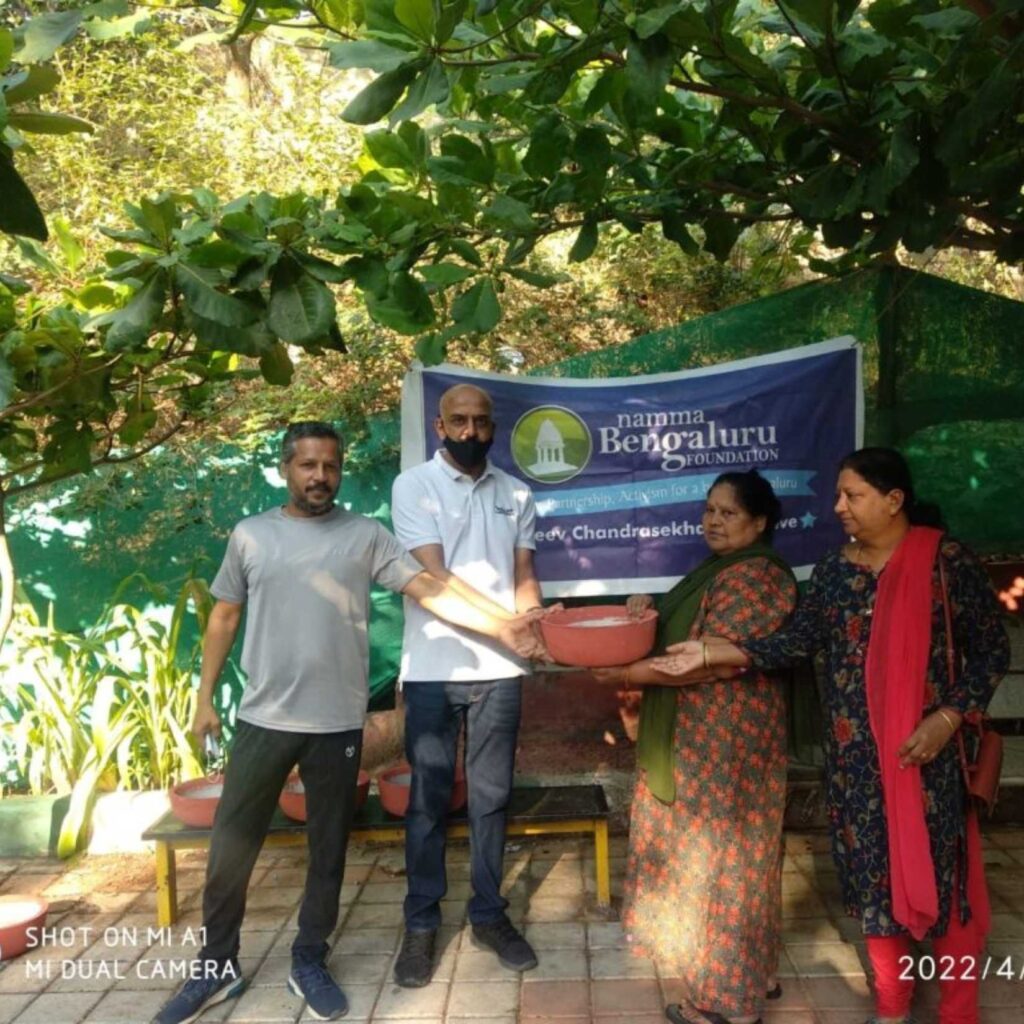

Cities in India, such as Bengaluru (Bangalore), have taken proactive steps to enhance urban green spaces through initiatives like the “Namma Bengaluru Foundation” and community-driven projects such as tree planting drives and urban forest restoration efforts in places like Turahalli forest. These efforts aim not only to increase green cover and reduce pollution but also to provide recreational spaces for residents.
Moreover, Bengaluru has implemented comprehensive tree census programs to assess tree health and distribution. For example, recent data shows that Bengaluru has over 2 million trees, contributing significantly to air quality improvement and urban biodiversity. This information has guided initiatives like the “Greening Bengaluru” campaign, which emphasizes community-driven tree planting efforts and sustainable urban forestry practices. Such initiatives not only enhance environmental resilience but also foster community engagement and ownership of urban green spaces, thereby creating healthier and more resilient urban environments.
To enhance the impact of tree census initiatives, cities can prioritize the integration of green infrastructure into urban planning frameworks. This includes expanding tree cover in marginalized neighborhoods with limited green spaces, implementing green roofs and vertical gardens in densely built areas, and fostering partnerships with local communities for tree maintenance and conservation efforts. Moreover, investing in urban forestry programs can create employment opportunities, promote environmental education, and strengthen the city’s resilience to climate change impacts.
By conducting tree censuses, urban planners can gather comprehensive data on where trees are located, their species diversity, and their health status. This information empowers them to make informed decisions about where to plant new trees and how to manage existing green spaces more effectively. For instance, cities like Bengaluru in India have utilized tree census data to identify areas with low green cover and prioritize tree planting initiatives to improve air quality and enhance urban biodiversity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, urban green spaces and trees are fundamental pillars in the development of sustainable and livable cities throughout India. As cities expand rapidly, the preservation and expansion of green areas such as parks, gardens, and tree-lined streets become increasingly crucial. These spaces not only provide aesthetic value but also deliver tangible benefits for residents’ well-being and environmental health. Urban greenery helps mitigate the urban heat island effect by cooling the environment and improving air quality through the absorption of pollutants. This, in turn, reduces the incidence of heat-related illnesses and respiratory diseases, enhancing public health outcomes. Moreover, green spaces support biodiversity by providing habitats for wildlife and promoting ecological balance within urban ecosystems.
By leveraging tree census data, cities can strategically plan for and manage their green infrastructure, identifying areas in need of additional greenery and implementing targeted greening initiatives. Continued investment in green infrastructure projects and active community involvement are vital to ensuring that urban environments in India remain resilient and inclusive, fostering a sense of community ownership and environmental stewardship among residents while securing a sustainable future for generations to come.

Written by
Anjeeta Goud
Team Business Development and Strategy
Terracon Ecotech
Reference:
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(17)32146-8/fulltext
https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/overview
https://www.namma-bengaluru.org/
https://wri-india.org/news/release-bengalurus-first-ever-climate-action-plan-launched
https://www.forestresearch.gov.uk/news/what-do-we-know-about-how-trees-can-cool-our-towns-and-cities/
https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/why-we-need-green-spaces-in-cities.html
https://www.usda.gov/media/blog/2020/06/03/tree-census-and-wealth-public-data
https://www.nycgovparks.org/trees/treescount/about
https://esgindia.org/greening-bangalore/index.html
https://www.savatree.com/whytrees.html