
The world is facing unprecedented environmental challenges, from climate change to biodiversity loss The construction and operation of infrastructure projects, such as dams, roads, and mines, are responsible for around 80% of global biodiversity loss, and the role of Environmental Management Plans (EMPs) and Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) has never been more critical. These tools help us understand and minimize the negative effects of our actions on the environment, but they face challenges such as lack of data, limited resources, and inadequate regulatory frameworks. Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for innovation and improvement, such as using digital technologies and integrating environmental considerations into development projects. Expore and learn more about EMP in our previous blog.

The environmental costs of human activities, such as pollution and climate change, are estimated to be around $4.7 trillion annually
According to our recent study, we have only 12 years to limit global warming to 1.5°C , and we’ve already lost 60% of the world’s wildlife populations since 1970. The rate of species extinction is 100 to 1,000 times higher than the natural rate (IPCC, 2019). By addressing the challenges and seizing the opportunities, we can create a more sustainable and equitable future for all. Learn why EIA is a mandatory requirement ?
The current rate of species extinction is 100 to 1,000 times higher than the natural rate
The field of EMPs and EIAs is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by emerging trends and challenges. trends are essential in identifying emerging opportunities, challenges, and best practices that can inform and improve environmental management and decision-making. Some of the key trends shaping the future of EMPs and EIAs include:

Digital technologies can reduce the time required for Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) by up to 50%

Digitalization and Technology :The increasing use of digital tools, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and geographic information systems (GIS), will revolutionize the way EMPs and EIAs are conducted. These technologies will improve data collection, analysis, and visualization, enabling more accurate and efficient assessments.
Integration with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):EMPs and EIAs will need to align with the United Nations’ 17 SDGs, ensuring that environmental management and impact assessments contribute to achieving sustainable development.
Increased Focus on Climate Change: As climate change becomes a growing concern, EMPs and EIAs will need to incorporate climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies, as well as assess the potential impacts of climate change on projects and operations.
Stakeholder Engagement and Participation: EMPs and EIAs will need to involve more extensive stakeholder engagement and participation, including indigenous peoples, local communities, and other affected groups.
Life Cycle Assessment and Circular Economy: EMPs and EIAs will need to adopt a life cycle approach, considering the environmental impacts of projects and operations throughout their entire life cycle, from design to decommissioning.
The traditional approach to Environmental Management Plans (EMPs) and Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) is plagued by inefficiencies, with manual processes leading to errors, delays, and increased costs. For instance, the lack of standardization, inadequate data management, and limited stakeholder engagement can result in inaccurate environmental impact assessments, delayed project timelines, and increased costs. Learn mandatory requirement of EIA in our latest blog ?
However, the integration of emerging trends and technologies, such as digitalization, artificial intelligence, presents a unique opportunity to transform the way EMPs and EIAs are conducted. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can improve the accuracy, efficiency, and transparency of environmental impact assessments, while reducing costs and enhancing stakeholder engagement. In fact, studies have shown that digital technologies can reduce the time required for EIAs by up to 50%, cut costs by up to 30%, and improve accuracy by up to 25%. Moreover, digital technologies can increase stakeholder engagement and participation in EIAs by up to 40%. By embracing these innovations, organizations can unlock significant benefits and drive sustainable development. Discover what is SIA?
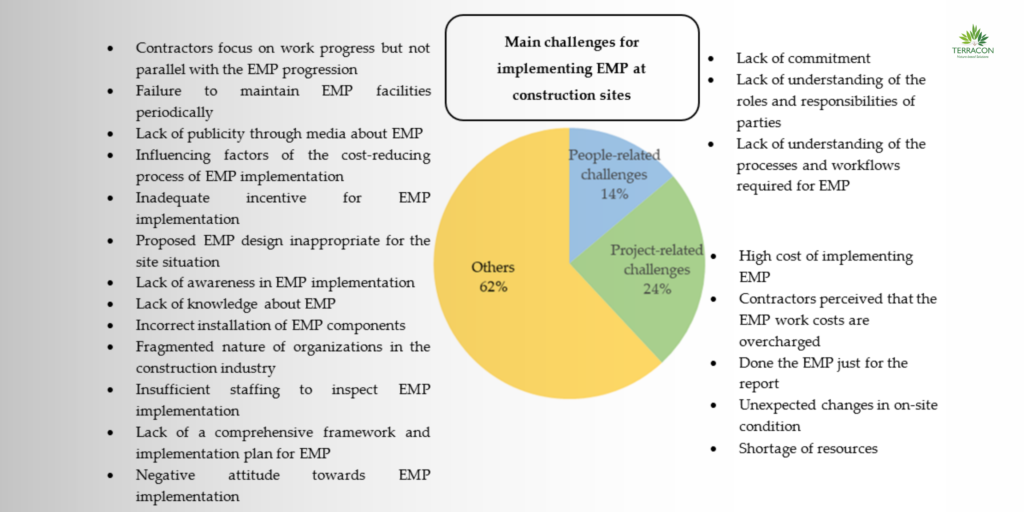
The adoption of Environmental Management Plans (EMPs) and Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) faces several barriers, hindering their widespread implementation. One major obstacle is the lack of standardization, which can lead to confusion and inconsistencies, making it challenging to compare and integrate results. For instance, in India, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has developed guidelines for EIAs, but the lack of standardization in reporting formats and data collection methods can make it difficult to compare the environmental impacts of different projects.
Another significant barrier is the insufficient resources required for the implementation of EMPs and EIAs, including funding, personnel, and technology. Many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India, for example, may not have the necessary resources to conduct comprehensive EIAs, making it difficult for them to comply with environmental regulations. Additionally, resistance to change can also slow the adoption of EMPs and EIAs, as some organizations may be hesitant to adopt new approaches and technologies. In India, for instance, some industries may be resistant to adopting sustainable practices, citing concerns about increased costs and reduced competitiveness. Finally, limited public awareness and understanding of EMPs and EIAs can make it difficult to engage stakeholders and secure support for environmental management and impact assessment initiatives. In India, for example, a survey by the Centre for Science and Environment found that only 22% of respondents were aware of the concept of EIAs, highlighting the need for greater public awareness and education on environmental issues.
In conclusion
The future of Environmental Management Plans (EMPs) and Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) is at a critical juncture. As we move forward, it is essential to harness the power of emerging trends, opportunities, and challenges to drive sustainable development and improve environmental outcomes. By embracing digital technologies, fostering collaborative stakeholder engagement, and integrating climate change considerations and circular economy principles, we can unlock the full potential of EMPs and EIAs. The time to act is now – let us seize this opportunity to shape a more sustainable future for all.

Written by
Anjeeta Goud
Team Business Development and Strategy
Terracon Ecotech
Reference :
(GIS), can revolutionize the way these assessments are conducted.




