In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, productivity and profit margins are often the primary focus. However, there’s a critical factor that frequently gets sidelined—the health of employees, particularly in relation to air pollution caused by industrial activities. As companies push to meet their goals, overlooking air quality can have hidden costs, affecting not just the well-being of employees but also the overall bottom line.
The Impact of Air Pollution on Employee Health
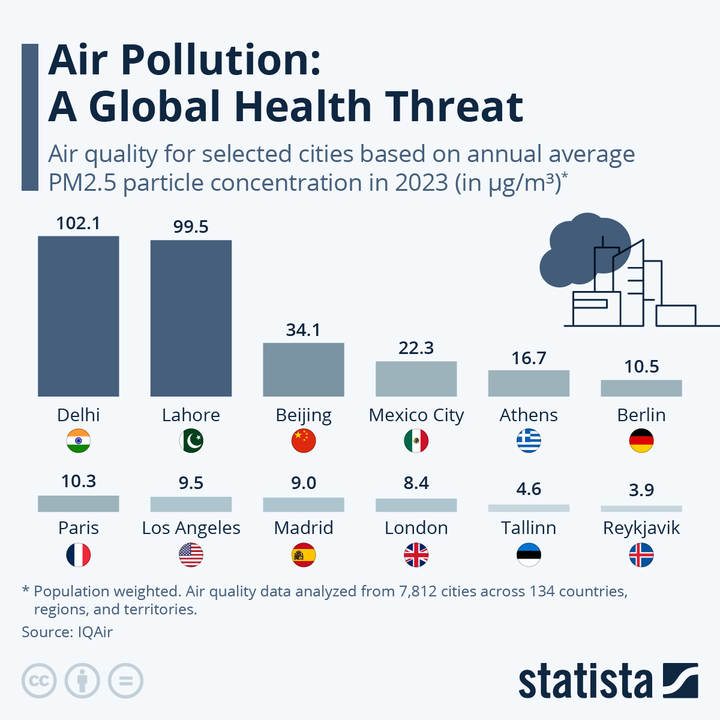
Air pollution is increasingly becoming a serious threat to public health and workplace productivity, especially in industrialized nations like India. As industries continue to grow, emissions from factories, power plants, and other sources lead to deteriorating air quality, which directly impacts employee health and efficiency.

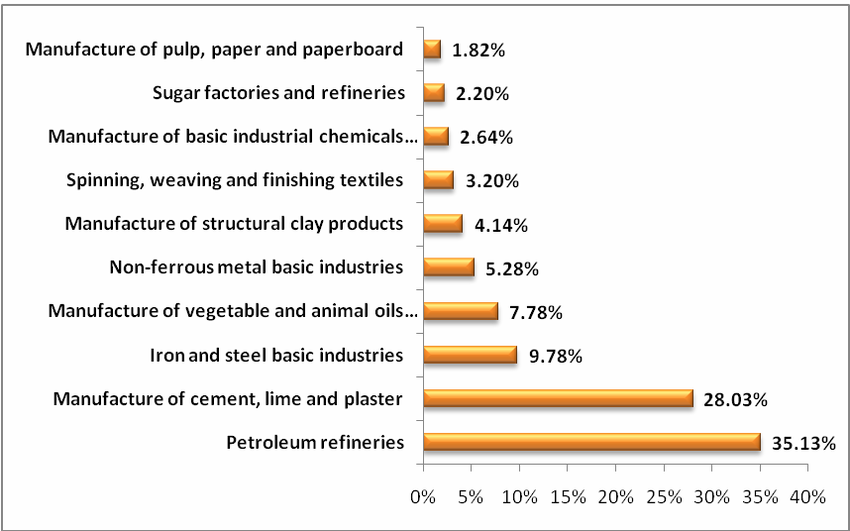
Let’s consider the manufacturing sector in India, which employs around 115 million workers. This sector presents a worrying scenario where many workers are routinely exposed to harmful pollutants such as particulate matter (PM2.5), sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. These pollutants, commonly released in industrial settings, can lead to a host of health issues including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Workers in textiles, construction, and similar industries are particularly vulnerable due to prolonged exposure. The chronic health issues that arise—like asthma, bronchitis, and cardiovascular diseases—are not just affecting individuals but are also leading to increased medical visits, long-term health complications, and in severe cases, premature deaths. This growing incidence of disease highlights the urgent need for improved workplace safety and stricter environmental regulations.
How Industries Contribute to Air Pollution
It’s no secret that industrial activities are a major source of air pollution. Manufacturing processes, transportation, and the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in various products contribute significantly to the degradation of both outdoor and indoor air quality. For instance, dust and particulate matter generated from construction, manufacturing, and even routine office activities can accumulate in the air and settle in workers’ respiratory systems, leading to serious health issues. Also learn why plastic should ban?
Chemical emissions are another major concern. VOCs released from paints, cleaning agents, building materials, and industrial processes can cause chronic health problems when inhaled over extended periods. Workers exposed to high concentrations of these chemicals often report headaches, dizziness, and respiratory issues. Poorly ventilated workspaces exacerbate the problem, trapping harmful substances indoors and creating an environment that directly impacts employee health and productivity.
The financial burden of air pollution is not limited to individual companies—it extends to the broader economy as well. A report suggests that air pollution could cost India up to 4.5% of its GDP by 2030 due to lost labor hours from issues like extreme heat and pollution. This statistic alone underlines the significant economic impact of poor air quality, particularly in industrial regions where workers are most exposed.
Economic Consequences for Companies
The economic consequences of neglecting employee health due to air pollution are substantial and far-reaching. Businesses that overlook the health impacts of air pollution are setting themselves up for significant financial losses. For instance, executives are already feeling the effects of climate change on their businesses in various ways. The rising cost of resources, cited by 34% of executives, can lead to increased costs for essential materials, higher operational expenses, and reduced profitability. Additionally, the risk of climate-related disasters has resulted in higher insurance premiums, with another 34% of executives noting increased costs or challenges in obtaining coverage. This financial strain can stretch budgets and divert resources from other critical areas.
Companies also face rising operational costs directly tied to healthcare expenses. As pollution-related health issues among employees become more prevalent, so too does the cost of providing healthcare benefits. This often leads to higher insurance premiums and greater financial strain on businesses. Moreover, the loss of productivity from absenteeism, where employees are unable to work due to illness, and presenteeism, where employees are present but not fully engaged due to poor health, can significantly hurt profitability.
Beyond immediate costs, there are long-term economic implications as well. Companies that fail to address the environmental impact of their operations may find themselves at a competitive disadvantage. As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, businesses that don’t prioritize reducing their environmental footprint could face reputational damage. Customers are increasingly likely to support companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and employee well-being, and those that don’t may experience decreased customer loyalty and a loss of market share.
Research also shows that air pollution can lead to immediate declines in worker productivity, even on days when pollution levels aren’t extreme. Studies have found that even small reductions in pollutants like PM2.5 can lead to measurable improvements in labor productivity. This indicates that even minor improvements in air quality can have a significant positive impact on worker efficiency and overall business performance.
Take the manufacturing sector, for example. Workers exposed to high levels of particulate matter often experience reduced efficiency and increased errors in their work. Textile workers in Tamil Nadu, for instance, have reported lower output on days with elevated pollution levels, which directly impacts production schedules and profitability. Similarly, agricultural workers in regions like Punjab suffer productivity losses due to air pollution, affecting their physical stamina and overall health. This combination of poor air quality and physically demanding work results in decreased yields, lower income, and a ripple effect that disrupts the entire supply chain.
Conclusion
The hidden costs of industrial expansion on employee health and efficiency are becoming increasingly clear. As air pollution continues to rise, its toll on both workers and businesses cannot be ignored. Companies that fail to address the environmental impact of their operations may face not only financial losses but also long-term damage to their workforce’s health and productivity. The economic and health-related consequences of air pollution serve as a stark reminder that employee well-being should be a priority in the pursuit of industrial growth and economic success.

Written by
Anjeeta Goud
Team- Business development and Strategy
Terracon Ecotech
Reference
Air pollution in India, focusing on industrial pollutants and their health effects on workers.
The health impacts of air pollution in India
Environmental factors, including air pollution, on worker productivity.\